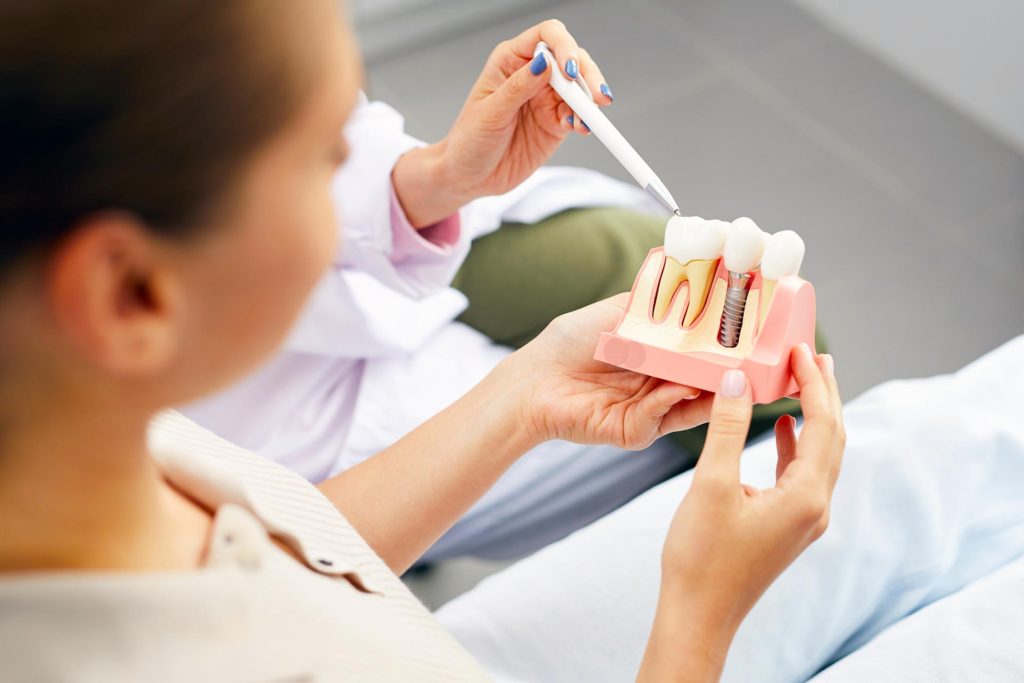
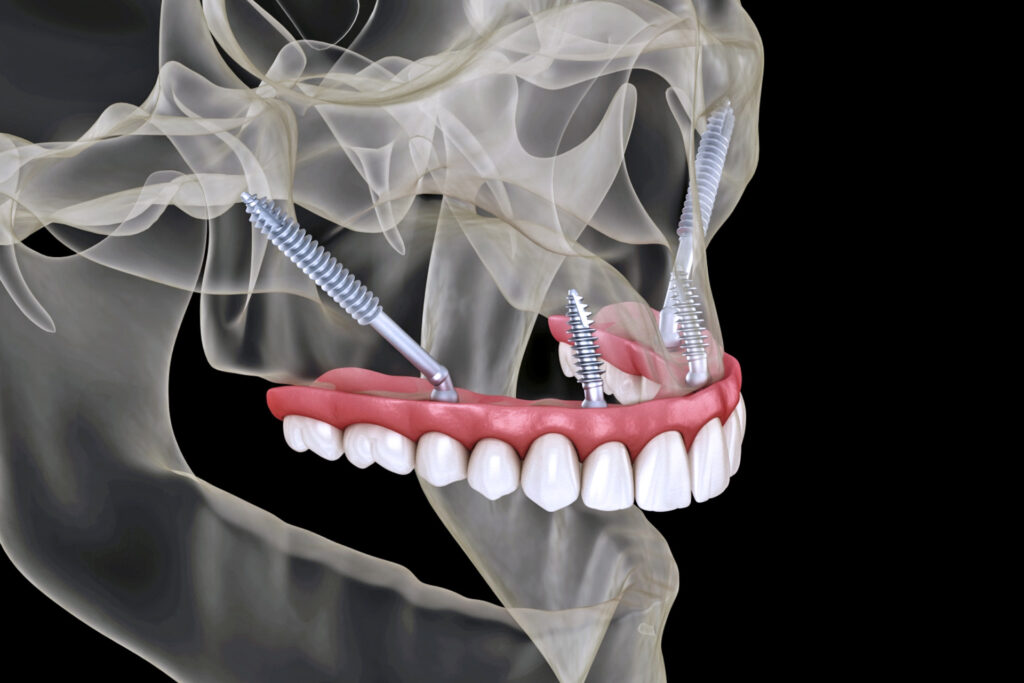
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are placed in the jawbone by imitating natural tooth roots in order to treat missing teeth. According to prosthesis or bridge alternative treatment methods; It is the closest application to the use of natural teeth in terms of biting, chewing and aesthetic appearance.
Neighboring teeth next to missing teeth do not need to be reduced. According to the physician’s decision; Pain during operations is controlled with local anesthesia, general anesthesia or sedation.
Metal, ceramic or polymer chemical compositions are used as implant materials from past to present. Polymer or ceramic materials are not preferred for long-term use as they are weak and brittle.
Implant material should be suitable for adequate mechanical resistance, biocompatibility, osseointegration and aesthetics. Titanium and Zirconia; They are the most preferred implant materials today due to their advantages in terms of static, dynamic and fatigue behavior. Fixed or removable dental prostheses placed on screwed tooth roots are decided according to the regional analysis of the missing teeth in the lower and upper jawbones.
Dental implants are preferred in patients with complete jawbone development. The average age at which bone development is completed is 17 years for women and 18 years for men. Since the treatment to be performed is a surgical intervention, the general health of the patient should be good. Implants are not suitable for patients with cardiovascular diseases (heart diseases, high blood pressure, etc.), endocrine diseases (obesity, diabetes, thyroid diseases, etc.), blood coagulation problems, pregnancy, and anatomical malformations in the jawbone. The patient should give information about the medicine or supplemental vitamins and minerals that he or she is currently using.
Treatment stages; It includes the removal of damaged teeth, making the jawbone suitable for the implant, placement of the appropriate implant, fusion of the bone with the implant (Osseointegration), placement of the bridge (connection element, abutment) and placement of the artificial tooth (crown).
Before treatment, clinical examination, radiological and 3D imaging techniques are used. The suitability of the bone tissue and whether the gums are healthy are checked. If the bone structure is thin or soft, bone tissue is strengthened by using natural or artificial implant bone graft materials.
Depending on the condition of the jawbone, the implants are screwed, if the jawbone is narrow and short, in the form of a plate, or when there is insufficient bone width-height, subperiosteal implant methods are appropriate. Subperiosteal implant helps to complete the treatment process faster by producing personalized implants with CAD/CAM modeling technology in digital environment without undergoing an orthopedic operation.
After the treatment, nutrition is important in the healing process of the gum tissue in order for the dental implant to fuse with the bone tissue. Very hot or very cold foods should not be consumed, soft foods should be preferred instead of hard and granular foods. Smoking and alcohol use may increase the risk of infection, prolonging the process, and may cause treatment failure. The surgical procedure takes a very short time, but since the treatment depends on the process of fusion of the implant and the bone, it takes 3-6 months with intermittent controls.